AUTONEWS
What is the useful life of an electric motor?
Whenever talking about electric cars powered by batteries, it is recurrent (and correct) to hear that they are vehicles that need less assistance, generating lower costs and fewer visits to the workshop. However, the topic of conversation quickly jumps to batteries, which insist on losing efficiency as the years (and kilometers) pass, seeing their capacity being limited by the treatment they are targeted and, above all, by the number of charges and discharges. But you never talk about engines. Are these infallible and will they last a lifetime? Nobody knows, but everything indicates that we will know soon.
To determine the useful life of an electric motor, depending on its type and the materials used, among other details, the Faculty of Vehicle Technology, at Esslinger University, decided to create a research project with a total cost of € 436,600 , in which € 314,630 is supported by the Research Foundation for the Application of Steel and the Association for the Research of Motor Technologies. There are also a number of car manufacturers involved in the project, essentially the three large local groups (BMW, Mercedes and Volkswagen), as well as automotive suppliers such as ZF, Mahle, Stiefelmayer Lasertechnik, Valeo Siemens eAutomotive, Schaeffler, Bosch, EM -Motive, AVL, Magna Powertrain, Voestalpine and Wälzholz.
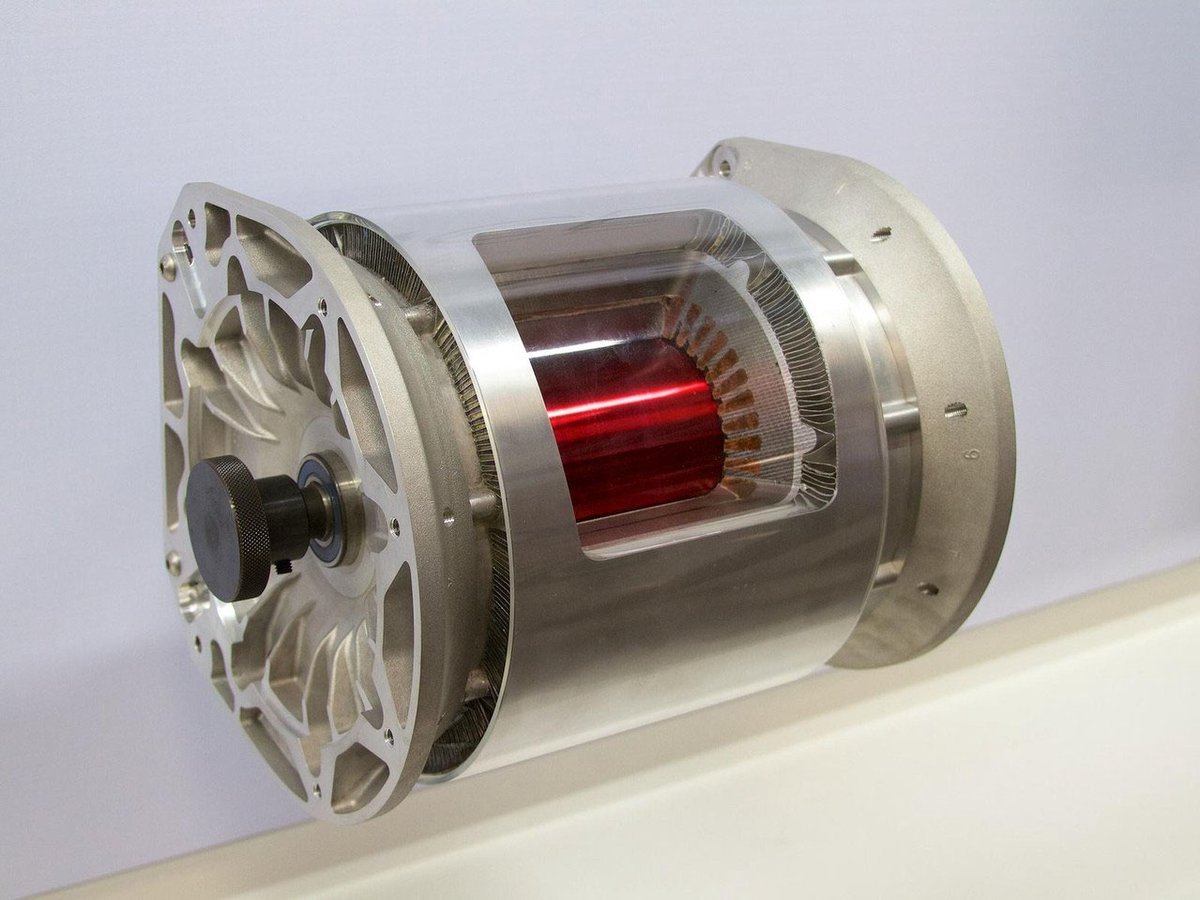
According to Professor Peter Häfele, of the said faculty, “the increasing use of electric motors in vehicles makes it imperative to develop methods to predict the useful life of their components”. The rotor, for example, is formed by several very thin layers (between 0.1 and 0.3 mm) of electric steel (a special iron alloy with magnetic properties), and it is necessary to determine how it is processed and constructed. “In the test that we are developing, there are several elements that condition the life of the rotor and that must be taken into account, from steel production to cutting, through rolling, further analyzing the effects of aging caused by temperature fluctuations and variations in temperature. load during operation, ”says Häfele.
Electric motors are extremely simple, limited to a rotor rotating inside a stator, transforming electrical energy into rotation. And they achieve an efficiency that, in some cases, can reach 97% (a combustion engine rarely reaches 40%), which means that there is only 3% of the energy consumed that is lost, especially in the form of heat.
There are several types of electric motors, but in cars two are mainly used, the induction motor on the one hand and the permanent magnet synchronous motor on the other. Both have advantages and disadvantages, but the second is more efficient (3 to 5%) than the first. See how Renault makes the Zoe's engine:
In a modern electric motor already without brushes, which wear out and require replacements, magnets or magnets are one of the essential parts, because in a driving unit of this type everything rotates due to magnetism and electric current. If there is no contact between the moving parts, there is no wear. Still, a user of this type of vehicle may wonder if the permanent magnet is really ... permanent.
According to rare earth experts, neodymium, the best of these elements for producing magnets, far exceeds the life of any vehicle. According to available data, a permanent magnet manufactured with neodymium loses an average of 5% every 100 years. That is, after 300 years of life, the magnets are still with 85% of the initial capacity to generate magnetic fields. There are those who question the importance of using electric steel of good quality and of controlled thickness in the construction of the rotor, for others to point out that the copper coil does not deteriorate over the years and kilometers, despite being the part of the responsible motor most (few) losses, due to the electrical resistance of the material. But there is a more vulnerable point in the electric motor.
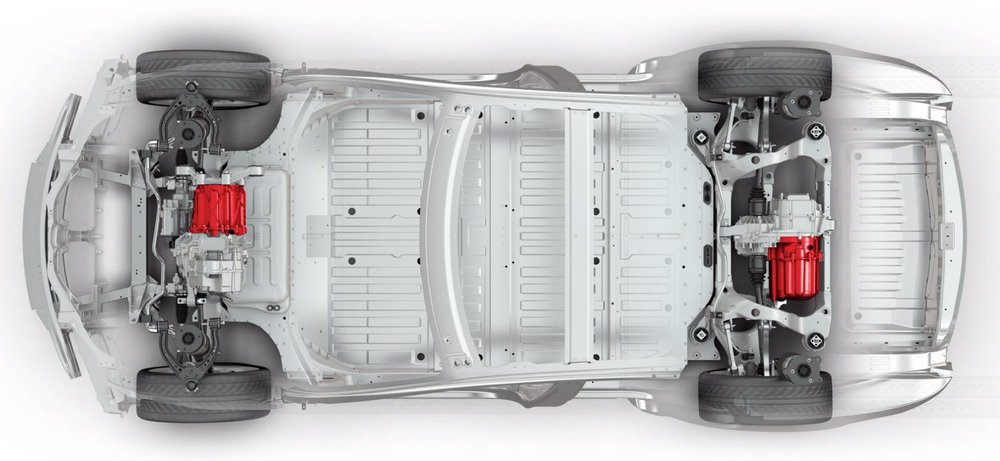

Like everything that revolves in this life, the rotor of the electric motor is also supported by bearings, which are relatively easy and cheap to replace. Of course, they are studied and prepared for the effort they will have to endure, which consists of having to rotate at around 20,000 revolutions in some cases, but it is guaranteed that they will not withstand 300 years of forced labor. Not likely 100 or 50 years old. In reality, nobody knows yet.
Until the conclusions of the study are known, what is expected to happen within three years, as well as the method that will determine the longevity of mechanics powered by electricity, know that an electric motor, if it fails, is highly more likely to do so while it is still new, with most of the faults being due to external electrical components, such as in the inverter.

Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário